LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高” 。
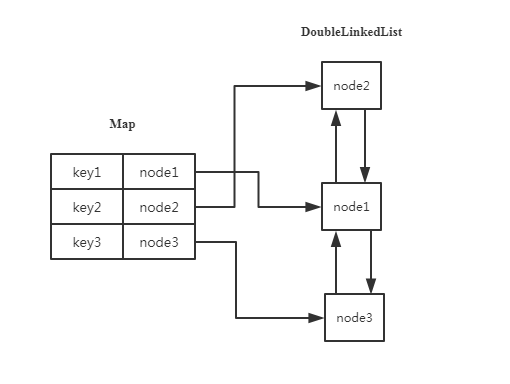
代码:
public class LRUCache {
private Map<Integer, DLinkedList> cache = new HashMap<>();
private int count;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedList head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.count = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.head = new DLinkedList();
this.tail = new DLinkedList();
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedList node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
removeNode(node);
addHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedList node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
node = new DLinkedList(key, value);
addHead(node);
cache.put(key, node);
count++;
if (count > capacity) {
DLinkedList preTail = tail.pre;
removeNode(preTail);
cache.remove(preTail.key);
count--;
}
} else {
node.value = value;
removeNode(node);
addHead(node);
}
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedList node) {
DLinkedList pre = node.pre;
DLinkedList next = node.next;
pre.next = next;
next.pre = pre;
}
private void addHead(DLinkedList node) {
DLinkedList next = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.next = next;
next.pre = node;
node.pre = head;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LRUCache cache = new LRUCache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
System.out.println(cache.get(1));
cache.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(cache.get(2));
cache.put(4, 4);
System.out.println(cache.get(1));
System.out.println(cache.get(3));
System.out.println(cache.get(4));
}
}
class DLinkedList {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedList pre;
DLinkedList next;
public DLinkedList() {};
public DLinkedList(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
|

